Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
Pellet 3D Printing Overview
What is Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)?

Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS), is a thermoplastic polymer that is widely used in various industries for its desirable combination of properties, processability, and price. It is a terpolymer, meaning it's composed of three different monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene.
ABS Mechanical Properties

Mechanical Strength
ABS has good mechanical properties, offering a balance of strength and flexibility. It can withstand impacts and loads without easily breaking or deforming.
Ease of Processing
This material can be easily molded and extruded, making it a popular choice for injection molding, 3D printing, and other manufacturing processes.

Chemical Resistance
ABS is resistant to certain aqueous solutions, alkalis, concentrated hydrochloric and phosphoric acids, as well as animal, vegetable, and mineral oils.
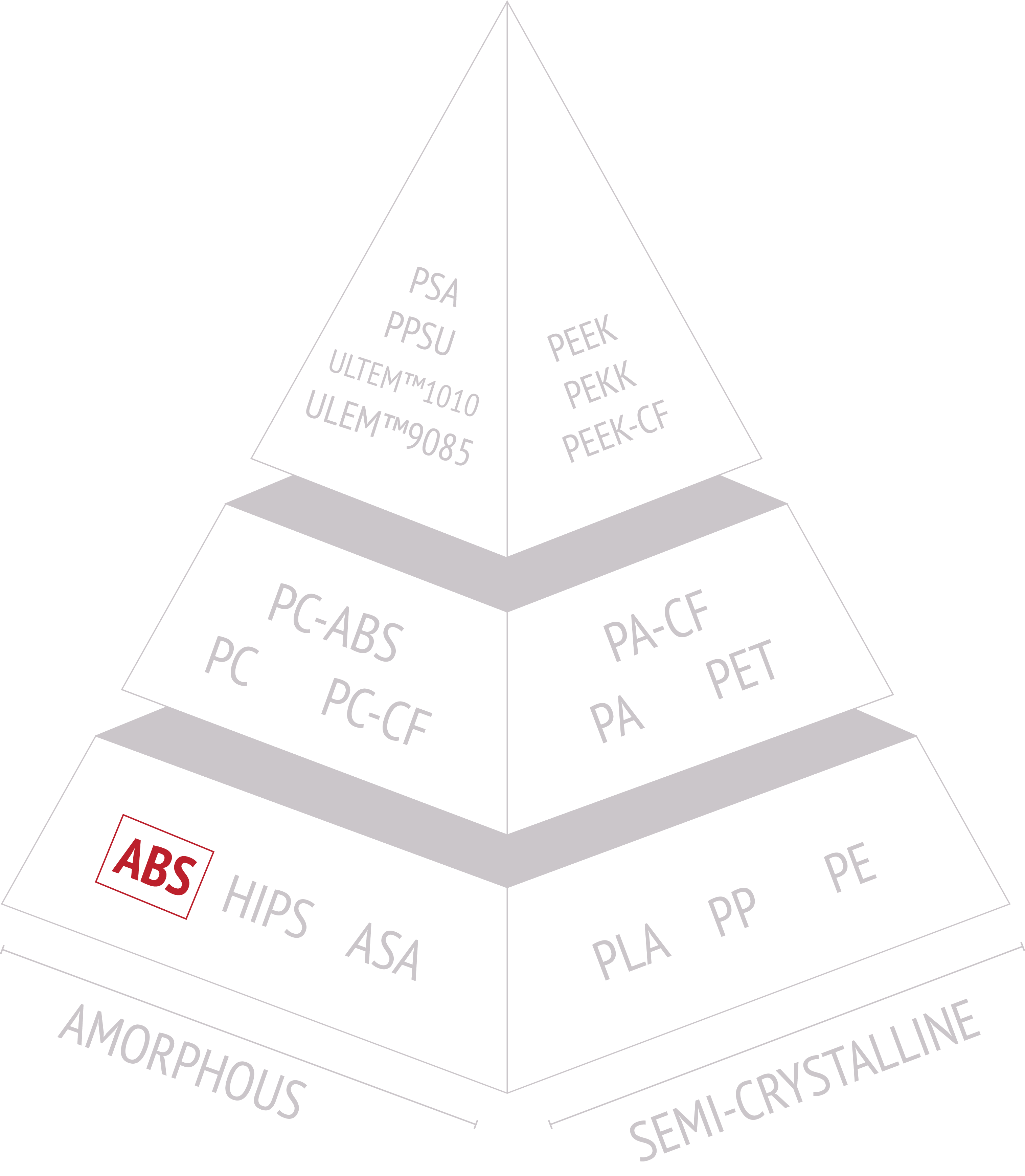
Is ABS Semi-Crystalline or Amorphous?
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) is considered to be an amorphous thermoplastic polymer. Amorphous polymers do not have a regular, ordered crystalline structure, and their molecular chains are arranged in a random fashion.
As a result, amorphous polymers tend to have a more transparent appearance and different mechanical properties compared to semi-crystalline polymers.
This amorphous nature contributes to ABS's desirable properties such as impact resistance, ease of processing, and good surface finish.
Common Names for ABS
Lustran is a trade name associated with ABS resins produced by INEOS Styrolution. They offer a range of ABS grades for different applications, like household appliances, sanitary equipment, and toys.
Cycolac is a well-known brand of ABS produced by SABIC (Saudi Basic Industries Corporation). It's used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, consumer goods, and electronics.
Magnum is a trade name for ABS resins produced by Trinseo. These resins are made using Trinseo’s proprietary polymerization technology, and are marketed to have an excellent white base color, low VOC levels, better aesthetics, and widened processing windows.
ABS Applications
ABS can be found across various industries as it is a general-purpose material fit for high degrees of tooling and end-use part applications.

Automotive Components
Used to create automotive parts such as interior panels, dashboard components, and exterior trim pieces. Its ability to handle temperature variations and mechanical stress is beneficial in this context.
Industrial Parts
ABS's combination of toughness and impact resistance makes it suitable for creating functional parts that need to withstand mechanical stress, such as gears, enclosures, housings, and brackets.

Electronics
Electrical insulation properties make it suitable for creating cases for electronic devices, as well as brackets and supports for wiring and components.
Tooling & Manufacturing Aids
In industrial settings, ABS can be used to create jigs, fixtures, tool handles, and other components required for manufacturing processes.
Challenges in printing
Ventilation & Fumes
ABS emits potentially harmful fumes during printing due to the release of volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Printing ABS in a poorly ventilated area can lead to unpleasant odors and potentially health risks. If you don't have proper ventilation or a dedicated enclosure with filtration, you might want to consider other materials.
Sensitivity
ABS is more sensitive to temperature differences while printing than other materials, like PLA or PETG. Without an enclosure, you'll be exposing your 3D print to temperature variations. This can lead to warping, layer adhesion issues, and even curling.
Printing for success
Material Preparation & Drying
ABS pellets can absorb moisture from the air, leading to poor print quality and extrusion issues. It's crucial to dry the pellets before use. It is highly recommended to use a dedicated dryer to remove any moisture from the pellets at a temperature and time provided by the material supplier, which is generally around 70-80°C for a few hours.
Cooling
ABS doesn't respond well to excessive cooling, so you should minimize the use of cooling fans during the printing process. Cooling can cause layer adhesion issues and warping.
Safety
Printing with ABS involves the release of potentially harmful fumes, so ensure proper ventilation in your workspace. If possible, use a printer with an enclosed build chamber and a filtration system to minimize exposure to fumes.
TL:DR | ABS Summary

Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a general purpose thermoplastic ABS can be found across various industries as it is a general-purpose material fit for high degrees of tooling and end-use part applications. ABS is considered to be an amorphous polymer. As a result, amorphous polymers tend to have a more transparent appearance and different mechanical properties compared to semi-crystalline polymers.
This material can exhume hazardous fumes so taking smart safety precautions will lead to greater success when printing.