What is Fused Filament Fabrication?
Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) is an extrusion-based 3D printing technique that feeds continuous filament through a heated extruder. As the filament travels through the extruder’s heating zones, it begins to liquify and is deposited along a controlled path to build parts one layer at a time. It may also be referred to as ‘Fused Deposition Modeling’ or ‘Filament 3D Printing’.
What is 3D Printing?
3D Printing, also known as Additive Manufacturing, refers to a collection of processes where materials are selectively deposited along a digitally defined path, making a three-dimensional solid object of virtually any shape layer-by-layer. Compared to traditional manufacturing processes, 3D printing offers advantages in design freedom and doesn’t require specialty tooling for production, making it a great tool for prototyping and low volume production.
The ASTM Committee F42 on Additive Manufacturing Technologies publishes official terminology standard for the industry. There are seven process classifications for additive manufacturing, including Binder Jetting, Directed Energy Deposition, Material Jetting, Powder Bed Fusion, Sheet Lamination, Vat Photopolymerization, and Material Extrusion.
Material Extrusion Technology
Material Extrusion is an additive manufacturing process where material, typically a thermoplastic, is selectively deposited through a nozzle or orifice.
The Material Extrusion technique was invented in 1989 and is the second 3D printing process successfully commercialized. It's used to reliably produce prototypes, concept models, tooling (jigs, fixtures, etc) with a variety of plastics. Material Extrusion is a dominant player in the industry and continues to play a major role in additive manufacturing.
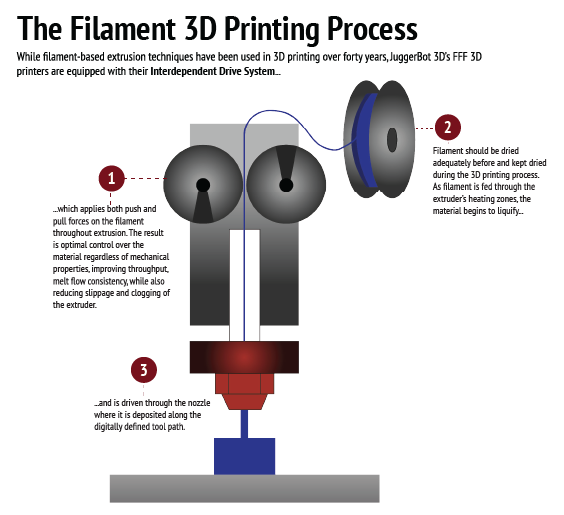
The Filament 3D Printing Process
Filament should be dried adequately before, and kept dried during the 3D printing process. As filament is fed through the extruder’s heating zones, the material begins to liquify and is driven through the nozzle where it is deposited along the digitally defined tool path.
3D Printing Filament
3D printing filament is a form of feedstock used in Fused Filament Fabrication. Filament is made through an extrusion process, usually from thermoplastic pellets, and is spooled onto reels. Filament is available in two standard sizes: 1.75 mm or 2.85mm diameter.
Many suppliers offer 3D printing filaments that can be used in machines with an "material agnostic" architecture. However, some machine builders "lock down" the materials that can be processed by their machines. Generally the latter requires operators to purchase filament from the machine builder, as well.
Comparing FFF & FGF
Fused Granulate Fabrication (FGF) is another popular material extrusion 3D printing technique. However, there are distinct differences between the two. Check out this page to learn more about the differences between each process, the difference in materials, and when to use one versus the other!
When to use Fused Filament Fabrication
FFF is typically best when used for:
- Small to medium part size
- Thin walls (< 2 mm / 0.08 in)
- Small features
- Low volume (1 – 1,000)
- Better aesthetic features (surface finish)
By using smaller nozzle sizes, depositing smaller bead width and smaller layer height, FFF technology will allow you to print thin-walled, highly complex parts.