NYLON (PA)
Pellet 3D Printing Overview
Explore the benefits of Nylon for pellet 3D printing, a high-temperature material characterized by multiple grades and industry applications.
What is Nylon?

Nylon (PA) is a type of synthetic polymer that belongs to the larger family of polymers known as Polyamides. These polymers are characterized by the presence of amide groups (CONH) in their chemical structure. Polyamides are often referred to as "nylons" when used as engineering plastics or textiles, as nylon is one of the most well-known and widely used types of polyamide.
Grades of Nylon
Polyamide comes in various grades due to its versatility and the ability to modify its properties to meet specific application requirements. The different grades of polyamide are created by adjusting the composition, additives, and manufacturing processes to achieve distinct sets of properties. While there are numerous grades of Nylon, these are three three most commonly used materials in the Additive Manufacturing market:
Nylon 66 (PA66)
Nylon 66 is known for its high melting point, chemical resistance, and stiffness. It's often used in applications requiring good heat resistance, such as automotive components, electrical connectors, and industrial equipment.
Nylon 6/6,6 (PA 6/6,6)
This is a widely used polyamide known for its excellent balance of strength, toughness, and ease of processing. It is commonly used in products like textiles, automotive parts, and engineering plastics.
Nylon 12 (PA12)
Nylon 12 is a flexible and tough polyamide with low moisture absorption. It is commonly used in applications requiring impact resistance, such as tubing for pneumatic systems, automotive components, and cable sheathing.
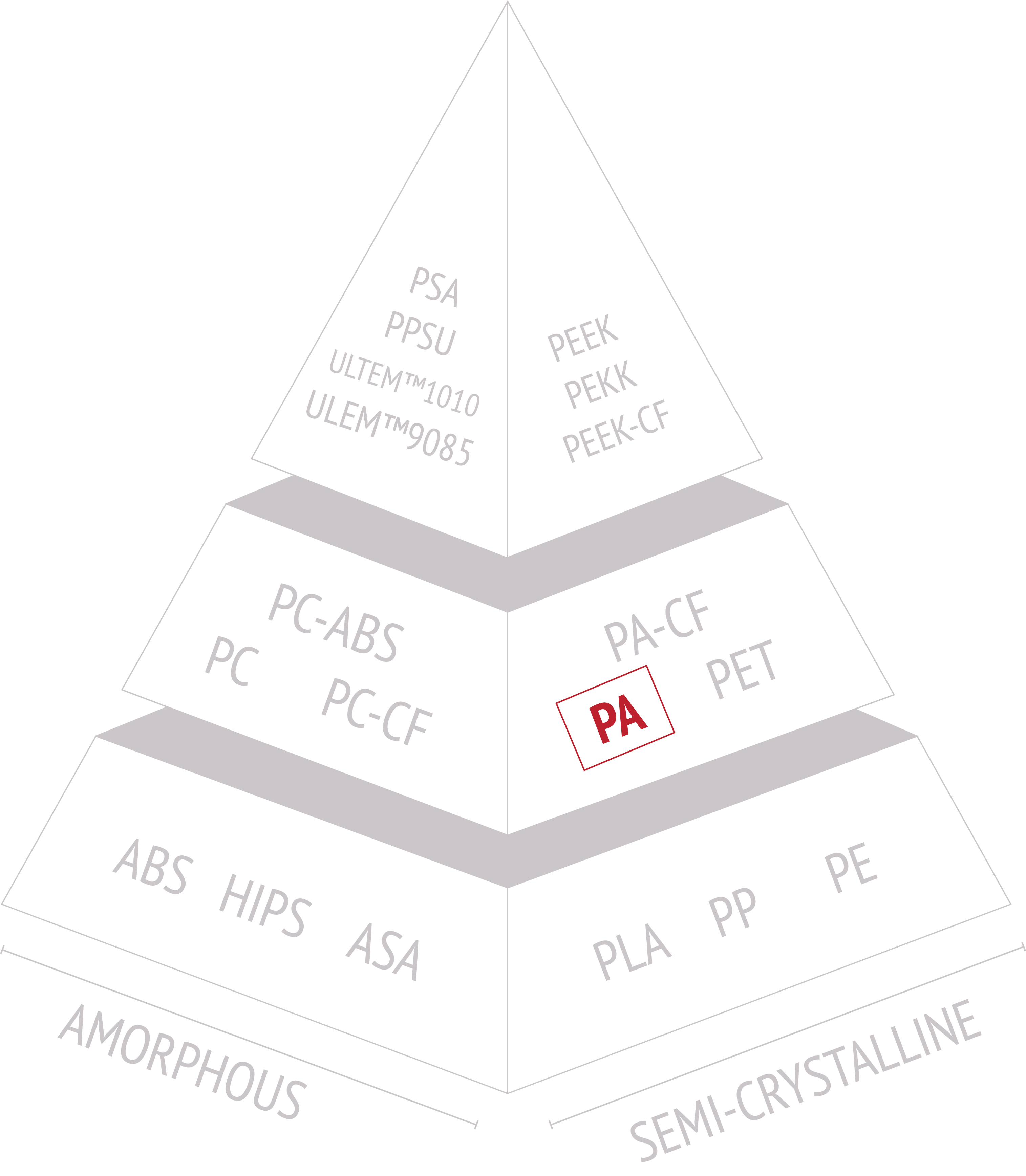
Is Nylon Semi-Crystalline or Amorphous?
Polyamide materials are typically semi-crystalline polymers. This means that they have a combination of both crystalline and amorphous regions in their molecular structure.
In a semi-crystalline polymer like polyamide:
- Crystalline Regions: These are highly ordered regions in the polymer's molecular structure where the polymer chains are neatly arranged in repeating patterns or crystalline structures. These regions contribute to the material's strength, stiffness, and some of its thermal properties.
The semi-crystalline regions in a specific polyamide grade can vary based on factors such as the type of polyamide (e.g., nylon 6, nylon 66, etc.), the processing conditions, and any additives or fillers included in the formulation. Polyamides can be tailored to achieve a desired balance of properties by adjusting the crystallinity and other structural characteristics through processing methods and formulation choices.
Nylon Mechanical Properties
Polyamide materials exhibit a range of properties that make them versatile and suitable for various applications. The specific properties can vary depending on the type of polyamide (e.g., nylon 6, nylon 66, nylon 11, etc.) and its formulation, but here are some general material properties associated with polyamides:

Tensile Strength
Polyamides have high tensile strength, meaning they can withstand significant pulling or stretching forces without breaking. This property makes them suitable for load-bearing applications.
Toughness
They are tough materials, which means they can absorb energy and withstand impacts without fracturing easily. This property is valuable in applications where resistance to mechanical shock is necessary.

Abrasion resistance
Ideal for products exposed to wear and friction, such as gears, bearings, and conveyor belts.
Challenges in printing
Pellet Moisture Content
Nylon is hygroscopic, which means it readily absorbs moisture from the environment. High moisture content in nylon pellets can result in poor print quality, including issues like bubbling, porosity, and weakened mechanical properties. Pellets must be properly dried before use.
Pellet flowability
The flowability of nylon pellets can vary depending on their properties and moisture content. Ensuring consistent and smooth flow through the printer's hopper and extrusion system is essential to prevent clogs and uneven extrusion.
Printing for success
Moisture Control
Nylon is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the environment, which can affect print quality. Proper drying of Nylon is a major key to have success in printing in a pellet-form.
Temperature
Precisely control the extruder and bed temperatures according to the manufacturer's recommendations for the specific nylon grade you are using. A temperature-controlled enclosure can help maintain stable printing conditions.
Layer Height & Print Speed
Experiment with different layer heights and print speeds to find the optimal settings for your specific nylon material. Nylon can benefit from slower print speeds to achieve better layer bonding
Nylon Applications
3D Printed Nylon can be found across various industries where high mechanical qualities are critical. Here are some specific applications for PEI in 3D printing:

Healthcare & Medical Devices
Nylon is used to 3D print custom prosthetic limbs and orthopedic implants, providing personalized solutions for patients.

Automotive Industry
Printed polyamide is used to create prototypes of automotive components, including engine parts, interior panels, and brackets, for testing and validation.
Manufacturing and Industrial Equipment
Nylon is used to create custom tools, fixtures, and jigs for manufacturing processes, enhancing production efficiency.

Aerospace & Defense
The lightweight nature of Nylon is beneficial in aerospace applications. It is used to produce lightweight structural components, drone parts, and satellite components.
TL:DR | Nylon Summary

Nylon, commonly found in a greater family of polymers called Polyamides (PA), is a versatile thermoplastic used in various applications. When in pellet form, nylon consists of small, granular particles of the polymer material. These pellets can be melted and processed through techniques such as injection molding, extrusion, and 3D printing to create a wide range of products. Key characteristics of nylons are high strength, temperature resistance, and excellent wear resistance that provide benefits across several industries. properties compared to semi-crystalline polymers.
This material can exhume hazardous fumes so taking smart safety precautions will lead to greater success when printing.