Polyetherimide (PEI)
Pellet 3D Printing Overview
What is Polyetherimide (PEI)?

Polyetherimide (PEI) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic that is known for its exceptional thermal, mechanical, and chemical properties. It is part of the polyimide family of polymers and is widely used in various industries due to its unique combination of characteristics. PEI is valued for its high heat resistance, mechanical strength, flame retardancy, and electrical insulating properties.
PEI Mechanical Properties
Heat Resistance
PEI exhibits excellent heat resistance, with a glass transition temperature (Tg) typically around 217°C (423°F). This property allows it to maintain its structural integrity at elevated temperatures, making it suitable for applications where exposure to high heat is a concern.
Mechanical Strength
This material is known for its high tensile strength, impact resistance, and stiffness. It can withstand mechanical stresses and loads, making it suitable for producing strong and durable parts.
Dimensional Stability
PEI has good dimensional stability over a wide range of temperatures, which is important for maintaining accurate shapes and sizes in different environments.
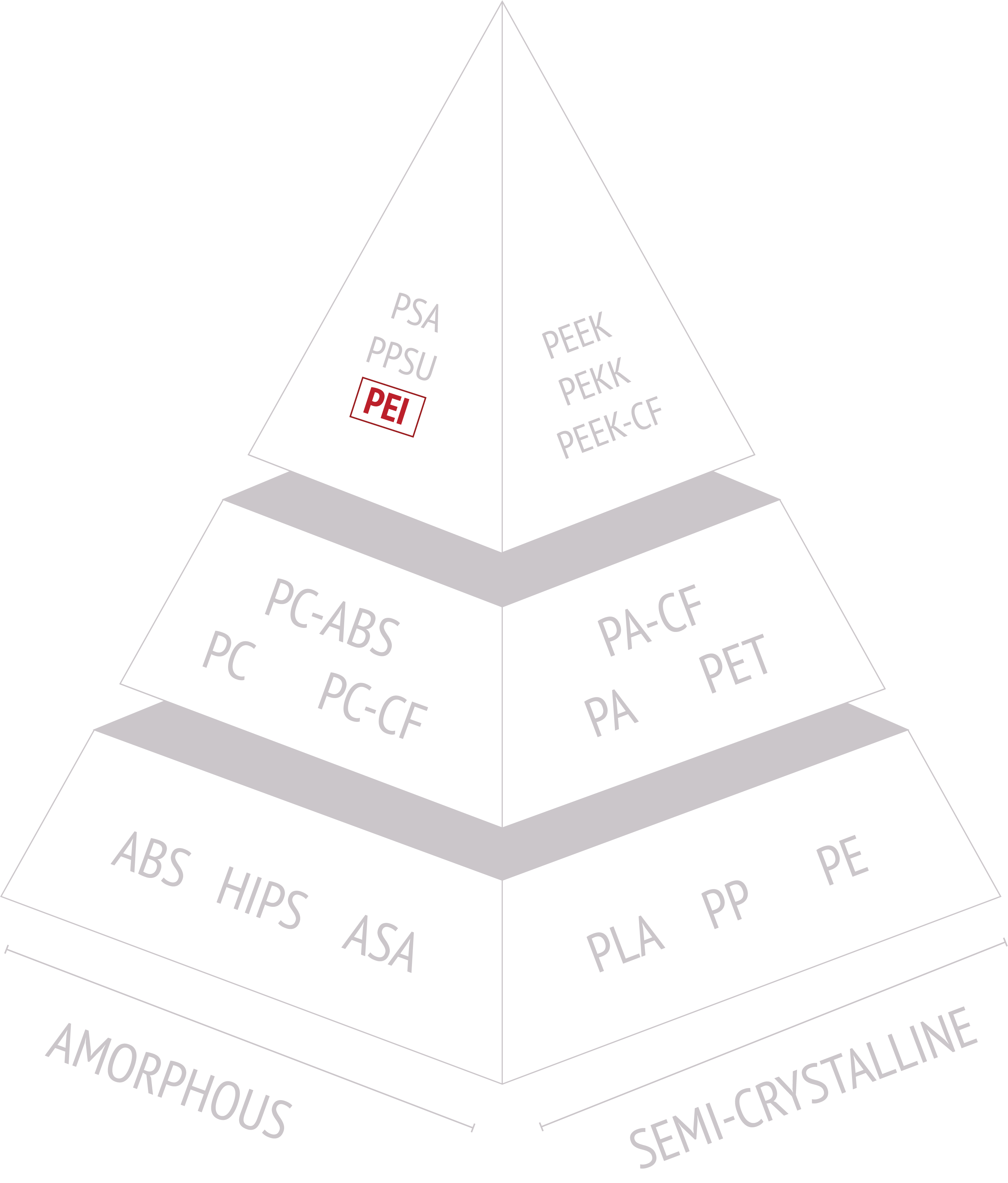
Is PEI Amorphous or Semi-Crystalline?
- Polyetherimide (PEI) is an amorphous thermoplastic rather than a semi-crystalline one.
- Amorphous polymers lack a well-defined crystalline structure and have a disordered molecular arrangement. This results in properties such as transparency, lower melting points, and more gradual transitions between solid and liquid states. PEI falls into this category, as its polymer chains do not exhibit a regular crystalline arrangement.
- While PEI is amorphous, it can be blended with other polymers or filled with additives to modify its properties, such as enhancing its crystallinity. However, the base PEI material is primarily used for its amorphous characteristics, including its high heat resistance, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation properties.
Common Names for Polyetherimide
Perhaps the most widely recognized trade name for PEI. It is produced by SABIC and is used in various industries for its high heat resistance, mechanical strength, and flame retardancy.
Offered by DuPont, is not precisely PEI, but rather a high-performance polyimide (PI) material with similar characteristics. It is known for its high-temperature and chemical resistance and is used in demanding applications such as aerospace and semiconductor manufacturing.
Trade name that encompasses a range of materials, including PEI, produced by the Glastic Corporation. These materials are often used for electrical insulation and other high-temperature applications.
PEI Applications
This material can be found across various industries where high mechanical qualities are critical. Here are some specific applications for PEI in 3D printing:

Aerospace Components
Aerospace industries benefit from PEI's high heat resistance and flame-retardant properties. 3D printed PEI parts can be used for interior components, ducting, brackets, and other non-critical flight hardware.

Automotive parts
PEI is suitable for producing automotive components that need to withstand high temperatures, such as under-the-hood parts, engine components, and custom accessories.

Electronics Enclosures
Strong electrical insulating properties make this an ideal material for 3D printing enclosures and housings for electronic devices that generate heat.

Energy
PEI's resistance to high temperatures and chemicals can be leveraged to produce components for the energy sector, including parts used in power generation and oil exploration.
Challenges in printing
Complex Geometries
Due to its tendency to warp, PEI may not be the best choice for complex geometries with large overhangs or intricate details that are prone to warping or poor adhesion.
Complex Geometries
PEI prints might require more post-processing steps to achieve a desired finish or mechanical properties. If you're looking for a simpler printing and finishing process, other materials might be more suitable.
Lack of Proper Equipment
PEI requires a 3D printer with a high-temperature extruder and a heated build plate capable of reaching and maintaining the required temperatures. If your printer doesn't meet these specifications, attempting to print with PEI could lead to poor results or damage to your printer.
Printing for success
Polyetherimide (PEI) can be challenging but rewarding when done correctly. To help you achieve successful PEI 3D prints, here are some tips and best practices:
Printer Combatability
Ensure your 3D printer is capable of reaching and maintaining the high extrusion and bed temperatures required for PEI (typically around 340-380°C for extruder and 100-120°C for bed).
Enclosed Chamber
If possible, use an enclosed print chamber or enclosure to maintain a stable printing environment, minimizing temperature fluctuations and reducing the risk of warping.
Post Processing Techniques
After printing, allow the print to cool on the bed before removing it to reduce the risk of warping due to rapid cooling. Sanding, polishing, or annealing can enhance the final finish and mechanical properties.
TL:DR | PEI Summary

Polyetherimide (PEI) is a high-performance engineering thermoplastic that is known for its exceptional thermal, mechanical, and chemical properties. It is part of the polyimide family of polymers and is widely used in various industries due to its unique combination of characteristics. PEI is valued for its high heat resistance, mechanical strength, flame retardancy, and electrical insulating properties.